
Table of Contents
Product development is a process of creating and bringing a new product to the market. It’s a complex process involving many variables. You have to convert an idea into a product, and the process usually involves a number of different people, practices, methods, systems, and environments.
During development, 80% of the cost of the product is defined. The process itself may be very expensive (for example, the development of a new plane can cost up to $10 billion). For all that, 25% to 50% (depending on the source) of the product development costs are wasted because the product is terminated before it is launched, or it fails in the market. Time may also vary: 30% of products take up to 6 months to develop, and 30% can take as much as 18 months to complete. That is why it is very important to organize the development process effectively, to avoid a product development life cycle that takes to long and to minimize quality issues.
Definition of the Product Development Life Cycle
The Product Development Life Cycle is a sequence of the activities required to plan, develop, manufacture and sell your product. Depending on the stages of your development process you have to focus on such activities as research, strategic planning, capital investment, engineering design, quality assurance, manufacturing, marketing.
Product Development Stages
According to product lifecycle management experts, there are 6 stages of new product development. Other concept models, like BAH Model or IDEO approach, offer fewer or more stages. In essence, they coincide with the PLM concept stages (but they’re classified in more or less in detail) and the sequence may vary.
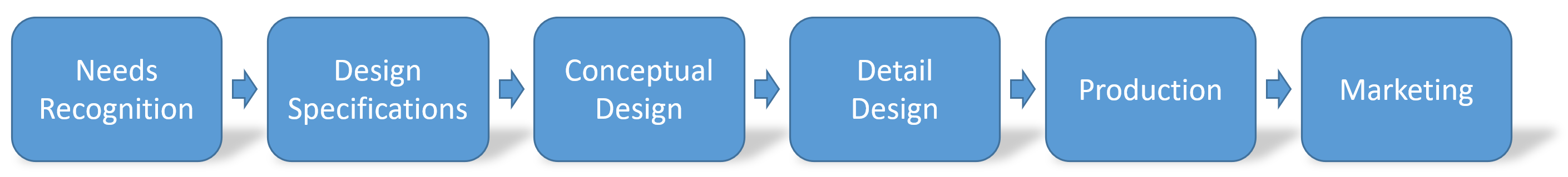
Stage 1. Needs Recognition
At this stage, information about customer needs is researched. External data, related to the discovered problems that the new product may resolve, is used to study consumer behavior.
Stage 2. Establishing Design Specifications
Innovators interpret the defined needs and formulate technical specifications. The required functionality of the product is defined. A specification contains the answers to the following questions:
- What are we going to create?
- What should we achieve in the end?
- How can we measure the results?
Stage 3. Conceptual Design
The company generates several alternative design options before defining their functionality and cost-effectiveness. Such characteristics of the new product are described:
- Usability,
- Styling,
- Technology.
The most marketable concept is selected.
Stage 4. Detail Design
The specifications are refined and the concept finalized. Component parts of the selected design concept are specified, and all the properties of the individual parts are planned: arrangement, forms, dimensions, surface properties. All the drawings are completed and production documentation is developed. When the design is completely described, proven and tested, a prototype model is produced.
Stage 5. Production
Manufacturing processes required to produce the selected items are identified, and manufacturing costs are assessed. Available technology and machinery should be utilized to ensure efficient and cost-effective production.
Stage 6. Marketing
Now product promotion and distribution to the target market happens. This stage includes planning proper, safe packaging and logistics details. In fact, marketing activities are performed right through the product development stage. Most companies start developing a marketing strategy even before the product design stage. Although, this work is done in the background. In the final stage of the product development cycle, marketing moves to the forefront.
Conclusion
The model of the product development life cycle is a structured plan of activities necessary to come up with a new product and release it. The 6 stages are needs recognition, establishing design specifications, conceptual and detail design, production, and marketing. Use this model to plan and consistently carry out the development of a new product.

